data breaches
Chinese State-Linked Hackers Target U.S. Internet Providers in Latest Cyber Espionage Campaign

In a concerning escalation of cyber espionage, a sophisticated group of hackers backed by China, known as “Salt Typhoon” or GhostEmperor, has been found infiltrating U.S. internet service providers (ISPs). This cyber campaign, attributed to state-sponsored actors, is indicative of a growing pattern of Chinese interest in U.S. critical infrastructure. The group gained unauthorized access to multiple ISPs, attempting to establish a persistent presence within these vital networks to gather intelligence, control data, and potentially disrupt essential services.
Who is Salt Typhoon / GhostEmperor?
Salt Typhoon, also called GhostEmperor, is part of a cohort of highly skilled cyber actors linked to the Chinese government. Known for its stealth, GhostEmperor uses advanced malware and tools to maintain hidden access to compromised systems. The group first gained significant attention in 2021 when cybersecurity experts from Kaspersky identified its operations targeting Southeast Asia, deploying a sophisticated rootkit called Demodex. GhostEmperor’s typical targets include government institutions, major infrastructure, and businesses within industries like telecommunications and technology.
The goal of Salt Typhoon’s attacks is to establish a foothold deep inside networks, allowing the group to operate undetected for long periods, siphoning off data or laying the groundwork for future attacks. This makes them particularly dangerous; they don’t just disrupt services but also potentially allow for ongoing surveillance and data exfiltration.
Details of the Recent Attack
The current attack, attributed to Salt Typhoon, has targeted a handful of U.S. ISPs by exploiting vulnerabilities within core network infrastructure, specifically targeting Cisco Systems routers. These routers play a critical role in managing internet traffic, and by compromising them, the attackers effectively gained access to much of the traffic flowing through these networks. This type of attack presents a national security concern, as ISPs are crucial to maintaining communication capabilities across the country.
Investigators, including cybersecurity teams from the affected ISPs and Microsoft’s threat intelligence division, believe the aim is to maintain a persistent presence. This persistent access allows Salt Typhoon to covertly harvest sensitive information, intercept communications, or disrupt services at critical times. This kind of intrusion allows attackers the ability to monitor network activities, extract information from data packets, and compromise the integrity of communication systems.
Microsoft has described the intrusion techniques used by Salt Typhoon as both advanced and evasive. The hackers are thought to have used zero-day vulnerabilities—flaws in systems that were previously unknown and, therefore, unpatched—making it exceptionally difficult for defenders to stop the breaches in real time.
History and Techniques of GhostEmperor
GhostEmperor is known for its use of customized rootkits and other tools designed to bypass detection by conventional security software. One of the notable tools in its arsenal is the Demodex rootkit, used to conceal malicious activities at the deepest levels of an infected machine. By gaining control at the kernel level (the core part of an operating system), the attackers can execute commands and control systems with minimal risk of detection.
The GhostEmperor group often uses command-and-control (C&C) servers to maintain contact with compromised devices. Once inside a network, the attackers plant malware to create backdoors—hidden entry points into systems—that provide ongoing access, allowing them to come and go undetected for extended periods.
This strategy was previously observed in attacks on countries like Malaysia, Vietnam, Thailand, and several others. These campaigns targeted government agencies, NGOs, and infrastructure, reflecting the broad scope of GhostEmperor’s objectives.
Recent Activity and Broader Implications
The latest campaign targeting U.S. ISPs is not an isolated incident. It comes amid a series of cyber attacks attributed to Chinese state-sponsored groups. Just days before the disclosure of this campaign, the U.S. government revealed it had disrupted a 260,000-device botnet called Raptor Train, controlled by another Chinese-linked group named Flax Typhoon. These botnets, often used for carrying out distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, also serve as a reminder of China’s capacity to harness enormous computing power for cyber operations.
The timing of these attacks aligns with increased geopolitical tensions and suggests a deliberate escalation by Beijing-backed cyber actors. By targeting ISPs, China-linked groups potentially gain access to valuable data, not only affecting individual users but also compromising the privacy and security of large-scale corporate and government communications.
The concern is not only the data that can be gathered but also the potential for manipulation. Access to ISP-level infrastructure means attackers could redirect traffic, intercept sensitive communications, and lay the groundwork for even more damaging future operations, such as shutting down parts of the internet during a critical incident.
Response from Authorities and Industry
The U.S. government has expressed growing alarm over the increasing frequency and sophistication of cyber attacks targeting critical infrastructure. As part of its response, the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) and the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) have been working alongside private companies, including Microsoft, to mitigate these threats. This collaboration involves sharing threat intelligence, rapidly patching vulnerabilities, and improving overall security postures across the industry.
Internet service providers are also being urged to implement stringent network segmentation—isolating different parts of their networks to limit the spread of any potential breach—as well as enhance their threat detection capabilities. Using artificial intelligence and machine learning to monitor network behavior can help identify anomalies that may indicate a security breach.
The Larger Cyber Conflict
The targeting of ISPs forms part of a larger strategy by China to gain strategic advantages over global adversaries through cyber warfare. Unlike traditional espionage, cyber operations can yield not just intelligence, but also opportunities to compromise the reliability and trustworthiness of communications infrastructure, potentially giving attackers leverage during geopolitical negotiations.
The current focus on critical infrastructure—telecoms, power grids, financial institutions—reflects the ongoing evolution in the tactics of state-sponsored actors. GhostEmperor, and other groups like it, represents a sophisticated blend of cybercriminal expertise and state resources, making them a significant challenge for cybersecurity professionals worldwide.
Conclusion
The recent infiltration of U.S. internet service providers by Salt Typhoon highlights a critical vulnerability in the nation’s infrastructure. As Chinese state-sponsored hackers become more adept at targeting key elements of communication networks, the risks to national security and economic stability grow. The response to such threats requires close collaboration between governments and private companies, rapid adaptation to emerging threats, and a robust commitment to securing the technology infrastructure that underpins the modern digital economy.
The actions of GhostEmperor underscore the critical need for constant vigilance, advanced defensive capabilities, and a coordinated global response to tackle the evolving landscape of cyber threats. As digital technologies continue to advance, so too must the efforts to protect them from those who seek to exploit their vulnerabilities.
data breaches
Cloudflare Outage Disrupts Global Internet — Company Restores Services After Major Traffic Spike

November 18, 2025 — MAG212NEWS
A significant outage at Cloudflare, one of the world’s leading internet infrastructure providers, caused widespread disruptions across major websites and online services on Tuesday. The incident, which began mid-morning GMT, temporarily affected access to platforms including ChatGPT, X (formerly Twitter), and numerous business, government, and educational services that rely on Cloudflare’s network.
According to Cloudflare, the outage was triggered by a sudden spike in “unusual traffic” flowing into one of its core services. The surge caused internal components to return 500-series error messages, leaving users unable to access services across regions in Europe, the Middle East, Asia, and North America.
Impact Across the Web
Because Cloudflare provides DNS, CDN, DDoS mitigation, and security services for millions of domains — powering an estimated 20% of global web traffic — the outage had swift and wide-reaching effects.
Users reported:
- Website loading failures
- “Internal Server Error” and “Bad Gateway” messages
- Slowdowns on major social platforms
- Inaccessibility of online tools, APIs, and third-party authentication services
The outage also briefly disrupted Cloudflare’s own customer-support portal, highlighting the interconnected nature of the company’s service ecosystem.
Cloudflare’s Response and Restoration
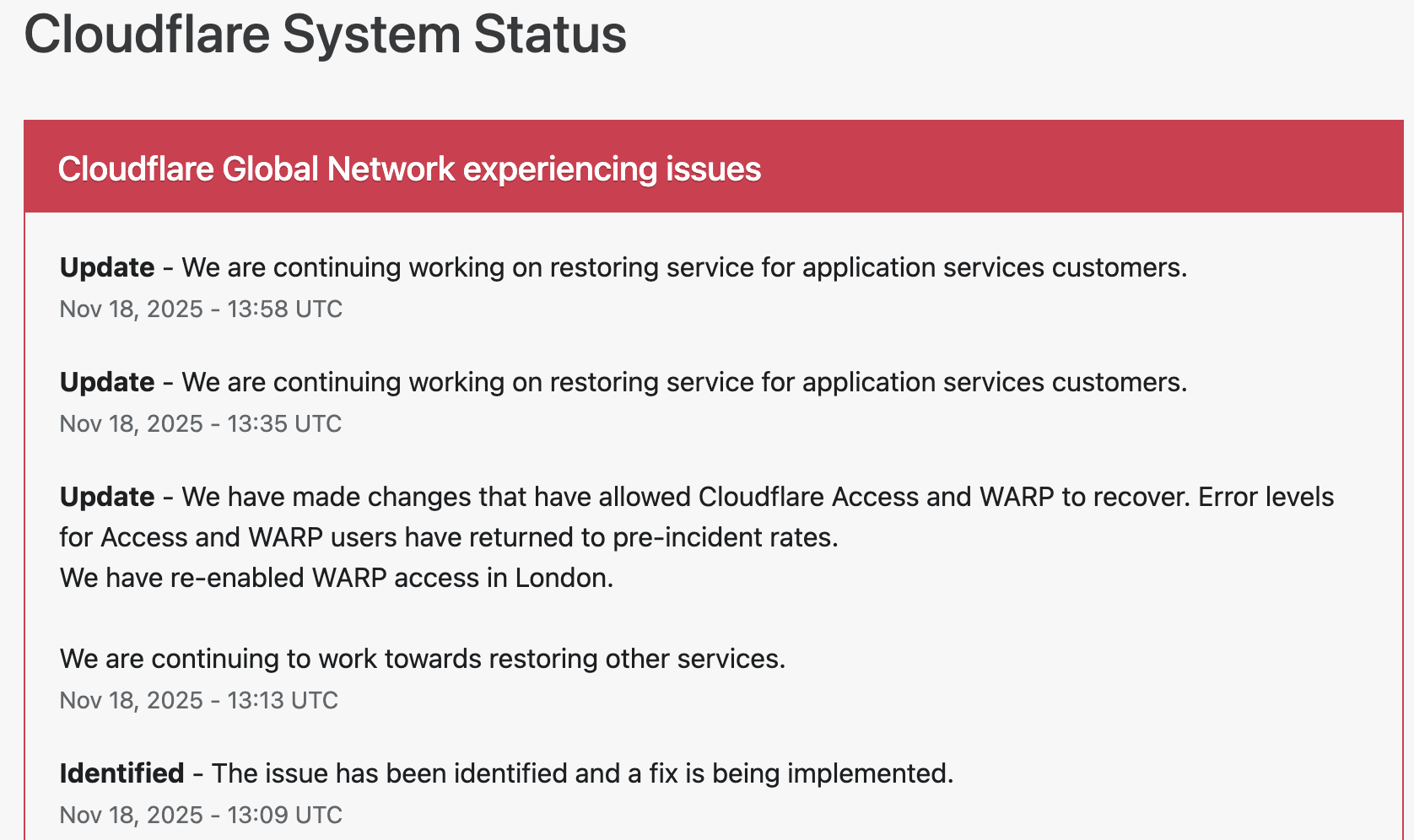
Cloudflare responded within minutes, publishing updates on its official status page and confirming that engineering teams were investigating the anomaly.
The company took the following steps to restore operations:
1. Rapid Detection and Acknowledgement
Cloudflare engineers identified elevated error rates tied to an internal service degradation. Public communications were issued to confirm the outage and reassure customers.
2. Isolating the Affected Systems
To contain the disruption, Cloudflare temporarily disabled or modified specific services in impacted regions. Notably, the company deactivated its WARP secure-connection service for users in London to stabilize network behavior while the fix was deployed.
3. Implementing Targeted Fixes
Technical teams rolled out configuration changes to Cloudflare Access and WARP, which successfully reduced error rates and restored normal traffic flow. Services were gradually re-enabled once systems were verified stable.
4. Ongoing Root-Cause Investigation
While the unusual-traffic spike remains the confirmed trigger, Cloudflare stated that a full internal analysis is underway to determine the exact source and prevent a recurrence.
By early afternoon UTC, Cloudflare confirmed that systems had returned to pre-incident performance levels, and affected services worldwide began functioning normally.
Why This Matters
Tuesday’s outage underscores a critical truth about modern internet architecture: a handful of infrastructure companies underpin a massive portion of global online activity. When one of them experiences instability — even briefly — the ripple effects are immediate and worldwide.
For businesses, schools, governments, and content creators, the incident is a reminder of the importance of:
- Redundant DNS/CDN providers
- Disaster-recovery and failover plans
- Clear communication protocols during service outages
- Vendor-dependency risk assessments
Cloudflare emphasized that no evidence currently points to a cyberattack, though the nature of the traffic spike remains under investigation.
Looking Ahead
As Cloudflare completes its post-incident review, the company is expected to provide a detailed breakdown of the technical root cause and outline steps to harden its infrastructure. Given Cloudflare’s central role in global internet stability, analysts say the findings will be watched closely by governments, cybersecurity professionals, and enterprise clients.
For now, services are restored — but the outage serves as a powerful reminder of how interconnected and vulnerable the global web can be.
data breaches
Cloudflare Outage Analysis: Systemic Failure in Edge Challenge Mechanism Halts Global Traffic
SAN FRANCISCO, CA — A widespread disruption across major internet services, including AI platform ChatGPT and social media giant X (formerly Twitter), has drawn critical attention to the stability of core internet infrastructure. The cause traces back to a major service degradation at Cloudflare, the dominant content delivery network (CDN) and DDoS mitigation provider. Users attempting to access affected sites were met with an opaque, yet telling, error message: “Please unblock challenges.cloudflare.com to proceed.”
This incident was not a simple server crash but a systemic failure within the crucial Web Application Firewall (WAF) and bot management pipeline, resulting in a cascade of HTTP 5xx errors that effectively severed client-server connections for legitimate users.
The Mechanism of Failure: challenges.cloudflare.com
The error message observed globally points directly to a malfunction in Cloudflare’s automated challenge system. The subdomain challenges.cloudflare.com is central to the company’s security and bot defense strategy, acting as an intermediate validation step for traffic suspected of being malicious (bots, scrapers, or DDoS attacks).
This validation typically involves:
- Browser Integrity Check (BIC): A non-invasive test ensuring the client browser is legitimate.
- Managed Challenge: A dynamic, non-interactive proof-of-work check.
- Interactive Challenge (CAPTCHA): A final, user-facing verification mechanism.
In a healthy system, a user passing through Cloudflare’s edge network is either immediately granted access or temporarily routed to this challenge page for verification.
During the outage, however, the Challenge Logic itself appears to have failed at the edge of Cloudflare’s network. When the system was invoked (likely due to high load or a misconfiguration), the expected security response—a functional challenge page—returned an internal server error (a 500-level status code). This meant:
- The Request Loop: Legitimate traffic was correctly flagged for a challenge, but the server hosting the challenge mechanism failed to process or render the page correctly.
- The
HTTP 500Cascade: Instead of displaying the challenge, the Cloudflare edge server returned a “500 Internal Server Error” to the client, sometimes obfuscated by the text prompt to “unblock” the challenges domain. This effectively created a dead end, blocking authenticated users from proceeding to the origin server (e.g., OpenAI’s backend for ChatGPT).
Technical Impact on Global Services
The fallout underscored the concentration risk inherent in modern web architecture. As a reverse proxy, Cloudflare sits between the end-user and the origin server for a vast percentage of the internet.
For services like ChatGPT, which rely heavily on fast, secure, and authenticated API calls and constant data exchange, the WAF failure introduced severe latency and outright connection refusal. A failure in Cloudflare’s global network meant that fundamental features such as DNS resolution, TLS termination, and request routing were compromised, leading to:
- API Timeouts: Applications utilizing Cloudflare’s API for configuration or deployment experienced critical failures.
- Widespread Service Degradation: The systemic 5xx errors at the L7 (Application Layer) caused services to appear “down,” even if the underlying compute resources and databases of the origin servers remained fully operational.
Cloudflare’s official status updates confirmed they were investigating an issue impacting “multiple customers: Widespread 500 errors, Cloudflare Dashboard and API also failing.” While the exact trigger was later traced to an internal platform issue (in some historical Cloudflare incidents, this has been a BGP routing error or a misconfigured firewall rule pushed globally), the user-facing symptom highlighted the fragility of relying on a single third-party for security and content delivery on a global scale.
Mitigation and the Single Point of Failure
While Cloudflare teams worked to roll back configuration changes and isolate the fault domain, the incident renews discussion on the “single point of failure” doctrine. When a critical intermediary layer—responsible for security, routing, and caching—experiences a core logic failure, the entire digital economy resting on it is exposed.
Engineers and site reliability teams are now expected to further scrutinize multi-CDN and multi-cloud strategies, ensuring that critical application traffic paths are not entirely dependent on a single third-party’s edge infrastructure, a practice often challenging due to cost and operational complexity. The “unblock challenges” error serves as a stark reminder of the technical chasm between a user’s browser and the complex, interconnected security apparatus that underpins the modern web.
data breaches
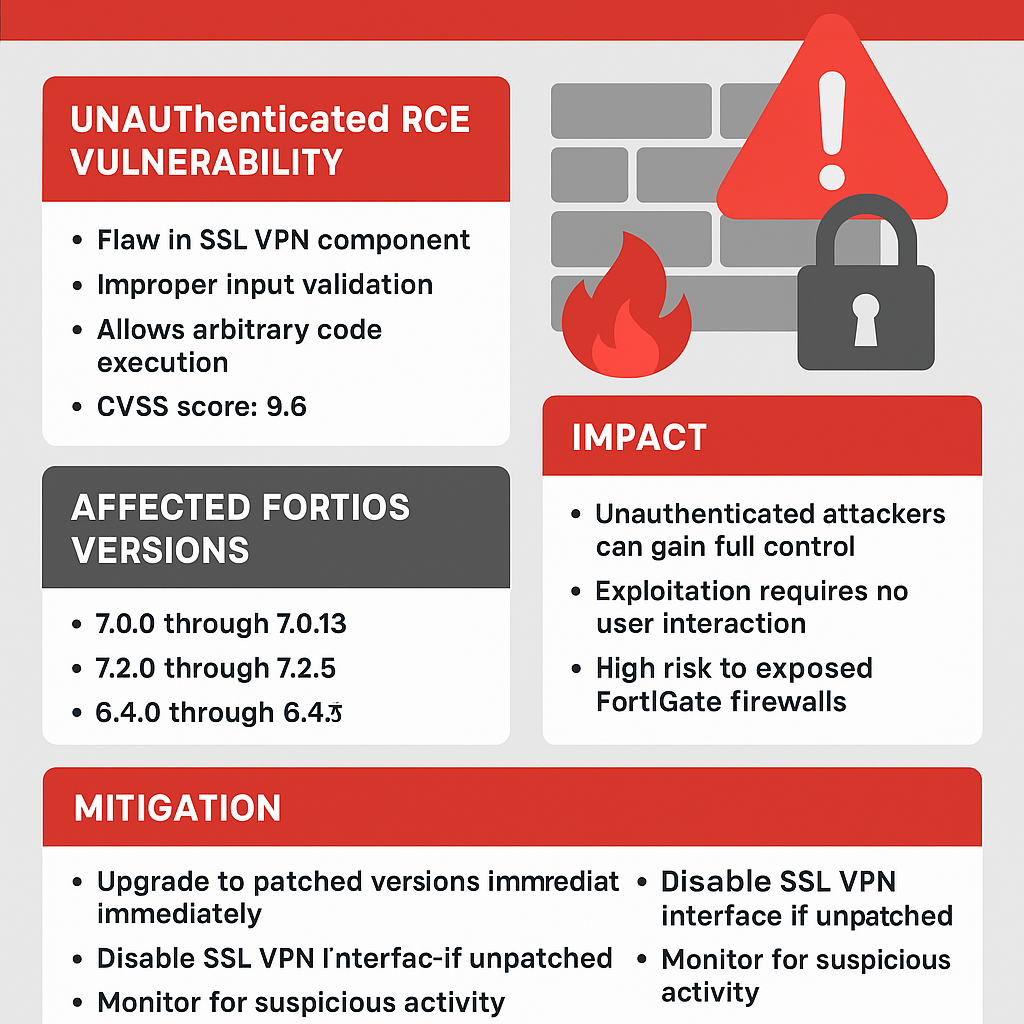
Manufacturing Software at Risk from CVE-2025-5086 Exploit

Dassault Systèmes patches severe vulnerability in Apriso manufacturing software that could let attackers bypass authentication and compromise factories worldwide.
A newly disclosed flaw, tracked as CVE-2025-5086, poses a major security risk to manufacturers using Dassault Systèmes’ DELMIA Apriso platform. The bug could allow unauthenticated attackers to seize control of production environments, prompting urgent patching from the vendor and warnings from cybersecurity experts.
A critical vulnerability in DELMIA Apriso, a manufacturing execution system used by global industries, could let hackers bypass authentication and gain full access to sensitive production data, according to a security advisory published this week.
Dassault Systèmes confirmed the flaw, designated CVE-2025-5086, affects multiple versions of Apriso and scored 9.8 on the CVSS scale, placing it in the “critical” category. Researchers said the issue stems from improper authentication handling that allows remote attackers to execute privileged actions without valid credentials.
The company has released security updates and urged immediate deployment, warning that unpatched systems could become prime targets for industrial espionage or sabotage. The flaw is particularly alarming because Apriso integrates with enterprise resource planning (ERP), supply chain, and industrial control systems, giving attackers a potential foothold in critical infrastructure.
- “This is the kind of vulnerability that keeps CISOs awake at night,” said Maria Lopez, industrial cybersecurity analyst at Kaspersky ICS CERT. “If exploited, it could shut down production lines or manipulate output, creating enormous financial and safety risks.”
- “Manufacturing software has historically lagged behind IT security practices, making these flaws highly attractive to threat actors,” noted James Patel, senior researcher at SANS Institute.
- El Mostafa Ouchen, cybersecurity author, told MAG212News: “This case shows why manufacturing execution systems must adopt zero-trust principles. Attackers know that compromising production software can ripple across supply chains and economies.”
- “We are actively working with customers and partners to ensure systems are secured,” Dassault Systèmes said in a statement. “Patches and mitigations have been released, and we strongly recommend immediate updates.”
Technical Analysis
The flaw resides in Apriso’s authentication module. Improper input validation in login requests allows attackers to bypass session verification, enabling arbitrary code execution with administrative privileges. Successful exploitation could:
- Access or modify production databases.
- Inject malicious instructions into factory automation workflows.
- Escalate attacks into connected ERP and PLM systems.
Mitigations include applying vendor patches, segmenting Apriso servers from external networks, enforcing MFA on supporting infrastructure, and monitoring for abnormal authentication attempts.
Impact & Response
Organizations in automotive, aerospace, and logistics sectors are particularly exposed. Exploited at scale, the vulnerability could cause production delays, supply chain disruptions, and theft of intellectual property. Security teams are advised to scan their environments, apply updates, and coordinate incident response planning.
Background
This disclosure follows a string of high-severity flaws in industrial and operational technology (OT) software, including vulnerabilities in Siemens’ TIA Portal and Rockwell Automation controllers. Experts warn that adversaries—ranging from ransomware gangs to state-sponsored groups—are increasingly focusing on OT targets due to their high-value disruption potential.
Conclusion
The CVE-2025-5086 flaw underscores the urgency for manufacturers to prioritize cybersecurity in factory software. As digital transformation accelerates, securing industrial platforms like Apriso will be critical to ensuring business continuity and protecting global supply chains.