education
Microsoft Addresses Deactivation Issue in Office 365 Applications

Microsoft has announced the release of a critical update to resolve persistent deactivation issues affecting its Office 365 suite, including popular applications such as Outlook, Teams, Word, and Excel. The issue, which led to sudden and unexpected deactivations for users, had caused widespread disruption for businesses and individuals relying on the platform for seamless productivity.
The Problem at Hand
Over recent weeks, Office 365 users reported a recurring glitch that prompted applications to deactivate unexpectedly. This issue often required users to repeatedly sign in or revalidate their licenses, causing significant interruptions to workflows and collaborative processes. Organizations that depend on uninterrupted access to tools like Teams for communication and Excel for data analysis were particularly affected.
The issue appeared to stem from discrepancies in license validation between the Office 365 applications and Microsoft’s cloud authentication services. As the problem grew, Microsoft acknowledged user complaints through its official support channels and committed to delivering a resolution promptly.
Microsoft’s Fix
In a blog post detailing the update, Microsoft confirmed the deployment of a software patch designed to eliminate the deactivation error. The fix, rolled out globally, ensures that Office 365 applications maintain consistent license validation without requiring frequent reactivation.
“We understand the frustration our users have experienced, and we have worked diligently to address this issue,” said a Microsoft spokesperson. “Our latest update aims to restore seamless access to Office 365 apps and uphold the productivity standards our users expect.”
How to Apply the Update
The fix is being distributed as part of the automatic update mechanism in Office 365. Users are encouraged to ensure their systems are set to receive updates automatically. For those who have disabled auto-updates, the patch can be manually downloaded and installed from Microsoft’s official website or through the application’s settings menu.
Microsoft has also released a comprehensive support guide to assist users who may continue to encounter issues despite the update. The guide provides step-by-step troubleshooting methods, including verifying account credentials, clearing cached data, and re-installing the Office suite if necessary.
User Feedback and Next Steps
Initial feedback from users who have applied the fix has been positive, with many reporting that the deactivation problem has been resolved. However, Microsoft has emphasized its commitment to monitoring the situation and addressing any residual issues.
To bolster transparency, the company has pledged to keep users informed through its service status dashboard and social media channels. Regular updates will ensure that users are aware of any additional steps they might need to take.
Implications for Businesses
The resolution of this issue is a welcome relief for businesses heavily reliant on Office 365 for their daily operations. With tools like Teams and Outlook at the core of remote work and collaboration, uninterrupted access is critical for maintaining productivity and meeting project deadlines.
As organizations transition back to normalcy following the update, IT administrators are advised to communicate the importance of regular updates to end-users and maintain proactive license management practices.
Looking Ahead
The quick resolution of this issue underscores Microsoft’s responsiveness to user concerns and its commitment to maintaining the reliability of its flagship productivity suite. As competition in the cloud-based productivity market intensifies, ensuring a seamless user experience remains paramount for retaining customer trust.
For more information or assistance with applying the update, users can visit Microsoft’s official support page or contact the company’s technical support team.
business
🇲🇦 King Mohammed VI’s Speech Sparks Heated Debate in Parliament — “جيل زد يُجيب”
Rabat — October 2025
Inside Morocco’s Parliament, tension and reflection filled the air just hours after His Majesty King Mohammed VI delivered his opening-session speech. What was meant as a national roadmap quickly turned into a day of open confrontation, emotional testimonies, and unexpected admissions from members of both majority and opposition blocs.
🏛️ A Speech That Touched Nerves
The King’s address, described by analysts as “direct and reform-oriented,” called for greater social justice, job creation, and balanced development across Morocco’s regions.
“No village left forgotten, no coast without a hand,” the King declared — a message that resonated deeply with citizens and lawmakers alike.
Within hours, parliamentary corridors buzzed with interviews, arguments, and introspection. Some MPs hailed the speech as “a moral reset,” while others questioned whether the government was capable of turning royal vision into tangible results.
🧠 From Rabat to the Sahara — Gen Z Responds
Younger members of Parliament — labeled as جيل زد (Gen Z) — became the focus of cameras and public curiosity. Many expressed frustration at what they see as a widening gap between political promises and everyday realities faced by Moroccan youth.
“The King spoke about unity and work. We agree — but the youth need a chance to prove themselves,” said one 28-year-old deputy.
“We have the energy; the system just needs to open its doors.”
Another young MP caused a social-media storm after saying that “in some ways, Moroccan social values are stronger than Germany’s.”
Critics accused him of downplaying Europe’s economic strength, while others applauded his pride in Moroccan family cohesion.
He later clarified his words, emphasizing that every nation faces challenges — and that Morocco’s real wealth lies in its people.
💬 Resignation, Reflection, and Responsibility
Just a week earlier, one deputy had submitted his resignation in protest over what he called “a lack of listening to the new generation.”
After the King’s address, he withdrew it.
“The royal speech gave me renewed hope. This is not the time to quit — it’s time to work,” he told reporters.
Across party lines, both RNI and PAM youth wings echoed similar messages: commitment to reform, but also impatience with bureaucracy.
Several MPs criticized ministers who, they said, “do not answer calls, do not reply to written questions, and have lost touch with citizens.”
⚖️ Opposition Voices: ‘A Government in Denial’
Members of the opposition used the session to accuse the cabinet of denial and poor communication, arguing that ministers are “living in a different reality” from citizens struggling with prices and unemployment.
“The royal messages were clear,” said one opposition leader. “The problem is not the King’s vision — it’s implementation.”
🌍 Morocco’s Path Forward
Analysts note that the King’s address aligned with long-standing themes: national cohesion, balanced territorial development, and respect for dignity in public service.
But the 2025 context — economic pressure, youth disillusionment, and the digital activism of Gen Z — gives these calls new urgency.
“This generation communicates differently,” said a policy researcher. “If institutions don’t adapt, they’ll lose credibility.”
🕊️ A Message Beyond Politics
As the parliamentary session ended, one young MP summed up the mood:
“الملك تكلّم… ونحن سنُجيب بالعمل — The King spoke, and we will answer through action.”
For now, the chamber that often echoes with partisan debates found itself united — briefly — under a single message:
Morocco’s future belongs to its youth, but responsibility belongs to everyone.
data breaches
GhostRedirector Exploit Hijacks 65+ Windows Applications
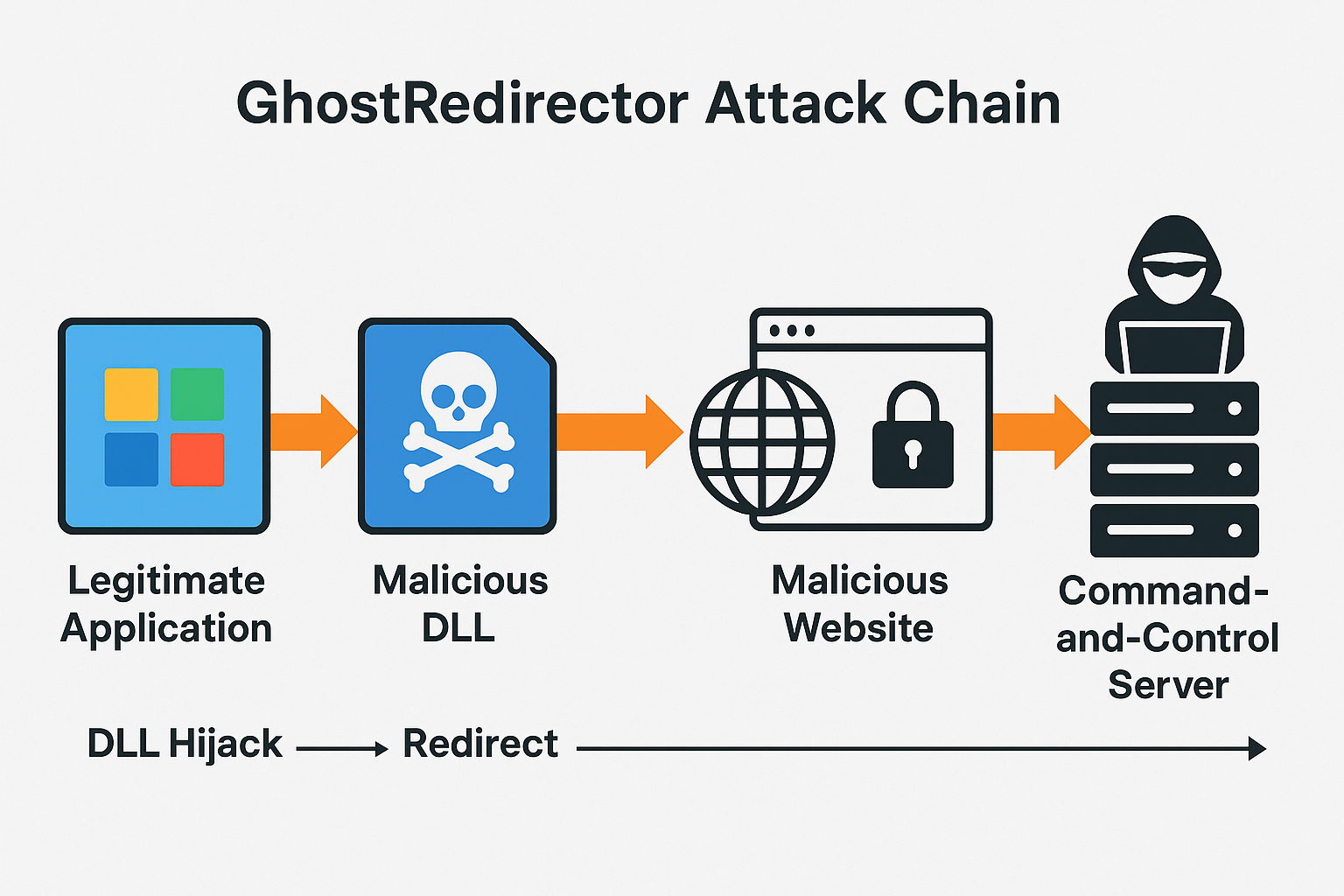
Cybercriminals abuse trusted Windows executables to redirect users, spread malware, and harvest sensitive data.
A new malware campaign dubbed GhostRedirector has compromised more than 65 legitimate Windows applications, weaponizing them to redirect users to malicious websites. Security researchers warn the large-scale abuse of trusted executables marks a dangerous escalation in software supply-chain exploitation, potentially impacting millions of users worldwide.
A sweeping cyberattack leveraging GhostRedirector has hijacked more than 65 popular Windows applications, turning trusted software into malicious redirectors that funnel users toward phishing sites, malware downloads, and credential theft operations, researchers said Friday.
Cybersecurity firm Trend Micro first documented the GhostRedirector campaign, which exploits Windows’ application behavior to quietly manipulate how programs connect to the internet. By injecting rogue instructions into legitimate executables, attackers can bypass traditional defenses and redirect traffic without raising user suspicion.
The targeted apps span a wide range of categories, including system utilities, multimedia tools, and office software, making the threat both widespread and stealthy. Researchers estimate that hundreds of thousands of machines could already be exposed.
“This is not just another malware strain—it’s a systemic abuse of trust in core applications,” said Ryan Flores, a senior researcher at Trend Micro. “Once attackers insert GhostRedirector hooks, users may never realize their favorite apps are weaponized against them.”
Technical Analysis
The hallmark of GhostRedirector is its ability to exploit DLL search order hijacking and application shimming techniques, both of which abuse the way Windows loads libraries during runtime:
- DLL Search Order Hijacking: Attackers drop a malicious dynamic-link library (DLL) in the same folder as a legitimate application. When the program runs, Windows prioritizes the local DLL, unknowingly executing the attacker’s payload.
- Application Shimming: By crafting malicious “shim” layers, attackers can alter how apps interact with the operating system, redirecting traffic or injecting malicious code without breaking the app’s normal functions.
- Persistence Mechanisms: GhostRedirector uses registry key modifications and scheduled tasks to ensure its redirect instructions survive reboots and updates.
- Command-and-Control (C2): Once a hijacked app redirects to attacker-controlled domains, the system communicates with a C2 server. From there, attackers can deploy secondary payloads like info-stealers, ransomware loaders, or spyware.
Researchers noted that the malicious DLLs are often disguised with names nearly identical to the original system files, making manual detection extremely difficult.
Impact & Response
The stealthy nature of GhostRedirector makes it particularly effective against enterprise networks:
- Phishing Campaigns: Redirected browsers load convincing login pages mimicking Microsoft 365, banking sites, and corporate portals.
- Malware Distribution: Users are tricked into downloading what appear to be updates, which are in fact droppers for ransomware or remote access trojans (RATs).
- Credential Harvesting: Once installed, the malware can extract stored credentials from browsers, email clients, and even VPN software.
Microsoft confirmed it is investigating, noting: “We strongly encourage customers to enable Defender for Endpoint advanced hunting queries and restrict the use of unsigned executables.”
- Ryan Flores, Trend Micro: “This is not just another malware strain—it’s a systemic abuse of trust in core applications.”
- Ciaran Martin, former head of the UK’s National Cyber Security Centre: “The exploitation of multiple widely-used apps is a classic supply-chain attack in miniature. The ripple effects could be profound.”
- El Mostafa Ouchen, cybersecurity expert and author of Mastering Kali Purple: “GhostRedirector shows that attackers are no longer focused only on vulnerabilities—they are hijacking functionality itself. Enterprises must implement behavioral anomaly detection and zero-trust execution policies to defend against such stealthy techniques.”
The attack echoes tactics from previous malware such as DLL SpyLoader and ShadowHammer, but at a much broader scale. Unlike traditional malware that infects via phishing emails or drive-by downloads, GhostRedirector piggybacks on the very executables users trust the most.
Security experts say this marks a dangerous evolution: while patch management addresses vulnerabilities, GhostRedirector proves attackers can weaponize functionality without relying on a CVE.
The GhostRedirector campaign illustrates a pivotal shift in attacker strategy: instead of exploiting flaws, they are exploiting trust. Experts believe this wave of attacks could accelerate global adoption of application allowlisting, endpoint monitoring, and AI-driven anomaly detection.
As Ouchen warned, “The battlefield has moved from patching vulnerabilities to monitoring behavior. The sooner enterprises accept that, the safer they’ll be.”
Sources:
This report is based on research published by Trend Micro, statements from Microsoft, and coverage by The Hacker News on the GhostRedirector campaign (September 2025).
data breaches
DeepSeek Breach Highlights Need for Stronger Cloud Security Posture

Wiz Research finds an exposed ClickHouse database with 1M+ log lines, including chat histories and secrets—spotlighting human error, weak access controls, and the need for DLP.
A misconfigured cloud database at Chinese AI startup DeepSeek exposed more than one million sensitive log lines, including chat histories and API keys, researchers said. The incident underscores how accidental data leaks can rival ransomware in impact. Experts urge least-privilege access, continuous cloud audits, and data loss prevention to curb escalating leak risks.
A publicly accessible DeepSeek database left over one million internal log entries exposed—revealing chat histories, secrets, and backend details—after a cloud misconfiguration granted broad access to a ClickHouse instance, according to researchers.
- Discovery & scope: Wiz Research identified a publicly exposed ClickHouse database tied to DeepSeek containing 1M+ log lines with sensitive data. The issue was reported and quickly secured.
- What was exposed: Logs included user chat histories, API/authentication keys, and backend system information—the type of data that can enable further compromise.
- Why it matters: The case illustrates how a single cloud configuration error can create full control over database operations for anyone who finds it.
Supporting details
- The Hacker News highlighted the leak as a cautionary example of preventable cloud data exposure and urged stronger governance around sensitive logs.
- Coverage by global outlets similarly stressed the ease of discovery and the potential for privilege escalation using exposed tokens and keys.
Context
The DeepSeek exposure caps a year of high-profile cloud misconfigurations across AI firms and SaaS providers, reinforcing that accidental leaks—not just ransomware—remain a top breach vector in 2025.
Quotes
- Wiz Research (blog statement):
“A publicly accessible ClickHouse database … allow[ed] full control over database operations.” - Independent industry summary (Wired):
“DeepSeek left … a critical database exposed … leaking system logs, user prompts, and … API authentication tokens.” - El Mostafa Ouchen, cybersecurity author and analyst:
“Data leaks are often preventable. Treat every log store like a crown jewel: remove public access, rotate secrets, and verify controls continuously—don’t wait for an attacker to do it for you.”
Technical Analysis
Likely cause & path:
- Misconfiguration: A ClickHouse endpoint exposed to the public internet without required authentication or network restrictions.
- Data at risk: Chat histories, internal system logs, API keys/tokens—high-value artifacts for lateral movement, session hijacking, and supply-chain pivoting.
- Attacker opportunities:
- Replay or abuse of API keys to access adjacent services.
- Prompt/log mining for sensitive business logic or PII.
- Privilege escalation by chaining leaked secrets with other weaknesses.
How to prevent this (practical controls):
- Block public access by default: Require private networking (VPC peering/PrivateLink), IP allowlists, and firewall rules for all database endpoints.
- Enforce authentication & authorization: Strong auth on ClickHouse; map service accounts with least-privilege roles; rotate keys regularly.
- Continuous cloud configuration audit: Use CSPM/CNAPP to detect internet-exposed DBs and misconfigurations in near-real time.
- Secrets hygiene: Centralize secrets in a vault; prohibit keys in logs; enable automatic rotation on exposure.
- Data classification & DLP: Tag log streams by sensitivity; apply DLP rules to block exfiltration to public destinations.
- Observability with guardrails: Alert on anomalous query volumes, mass exports, or schema enumeration; enable immutable logging.
- Tabletop & drill: Practice “open-DB” scenarios: discovery → containment (block ingress) → rotate keys → scope impact → notify.
(These recommendations align with lessons emphasized by Wiz and incident summaries.)
Impact & Response
- Affected entity: DeepSeek; researchers reported, and the company secured the database promptly after notification. It remains unclear if third parties accessed the data before closure.
- Potential downstream risk: Stolen tokens could enable follow-on intrusions into services integrated with the AI stack; leaked prompts/logs may reveal proprietary methods or customer information.
- Long-term implications: Expect regulators and customers to demand evidence of cloud control maturity (CIS, SOC 2) and richer audit trails for AI platforms. (Analytical inference grounded in cited reporting.)
- The report: The Hacker News’ explainer, “Detecting Data Leaks Before Disaster,” uses DeepSeek as a case study to argue for proactive detection of inadvertent leaks. The Hacker News
- Earlier coverage: Reuters, Wired, and others previously detailed the January 2025 exposure and the sensitivity of the leaked logs and keys. ReutersWIRED
Conclusion
The DeepSeek exposure shows how one toggled setting can turn a powerful AI stack into a liability. As AI adoption accelerates, misconfiguration-driven data leaks will remain a board-level risk. Closing the gap requires default-deny network posture, continuous config validation, disciplined secrets management—and the humility to assume something is already exposed. wiz.io